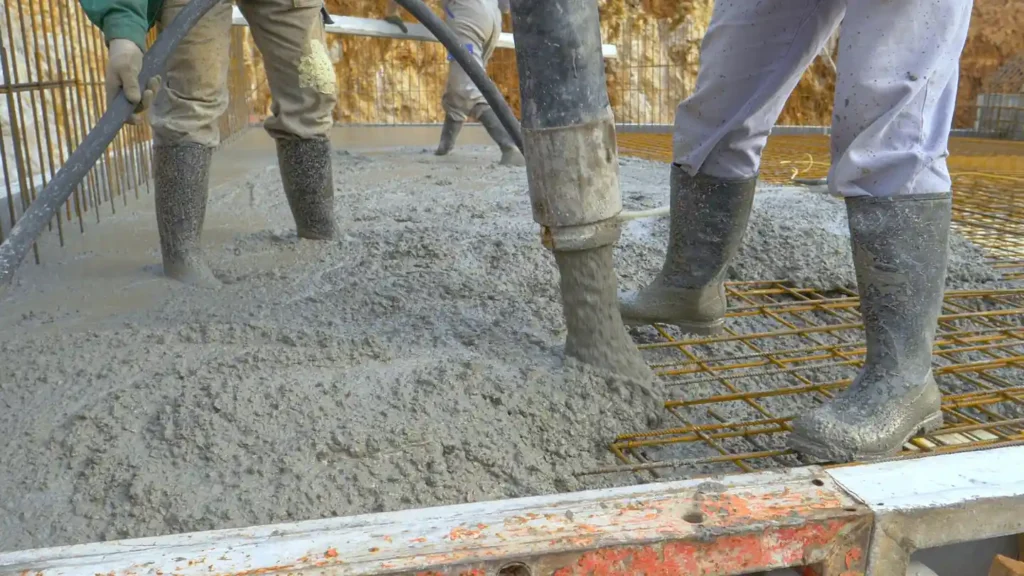
A comprehensive vapor mitigation project walkthrough, from initial assessment to final installation, involves a meticulously engineered process to safeguard multi-family residential developments from subsurface contaminants. This journey begins with data-driven site characterization, progresses through PE-stamped design, and culminates in precision installation, ensuring regulatory compliance and long-term protective efficacy. Understanding each phase is crucial for developers and general contractors navigating brownfield redevelopment or properties with identified vapor intrusion risks.
Phase 1: The Foundation of Remediation — Data-Driven Site Characterization
Every successful vapor mitigation project begins not with a shovel, but with rigorous data collection and analysis. This initial phase is critical for defining the scope of the problem and informing a precision-engineered solution. It’s about moving beyond assumptions to establish a clear, evidence-based understanding of subsurface conditions.
Comprehensive Site Assessment and Sampling
The cornerstone of effective mitigation is a thorough site assessment. This involves collecting soil gas, groundwater, and indoor air samples to identify the types and concentrations of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), methane, or radon present. Licensed professionals utilize specialized equipment and adhere to strict sampling protocols to ensure data integrity. The data gathered provides the essential parameters for system design, including contaminant plume characteristics, soil permeability, and groundwater depth. This meticulous approach ensures that the subsequent engineering is directly responsive to the site’s unique chemical and physical challenges. Regulatory fluency across various state environmental agencies guides these initial sampling plans, ensuring all efforts contribute to an actionable dataset.
Risk Assessment and Regulatory Interface
Once data is compiled, a detailed risk assessment evaluates potential exposure pathways and health risks to future occupants. This assessment quantifies the vapor intrusion potential, guiding the selection of appropriate mitigation strategies. Concurrently, experts engage with regulatory bodies to understand specific jurisdictional requirements. This proactive regulatory interface ensures that the proposed solution not only meets technical specifications but also secures necessary permits and approvals, avoiding costly delays. Understanding the nuances of state-specific guidelines, such as those from the California Contractors State License Board or specific EPA regional directives, is paramount.
Phase 2: Precision-Engineered Design — Developing the Mitigation Blueprint
With a robust dataset informing the site’s specific challenges, the next phase involves the development of a custom, PE-stamped mitigation system design. This is where sophisticated engineering translates raw data into a tangible protective solution.
System Selection and Component Specification
Based on the risk assessment and regulatory mandates, engineers select the most appropriate vapor mitigation technology. Common systems for multi-family developments include passive sub-slab depressurization, active sub-slab depressurization (ASD), sub-membrane depressurization (SMD), or vapor barrier systems. For example, a multi-story building might integrate a high-performance vapor barrier membrane beneath the foundation slab, coupled with a passive or active vent system to manage residual vapors. Each component, from the vapor barrier material (e.g., multi-layer polyolefin or HDPE) to vent pipe diameters and fan specifications for active systems, is precisely engineered to meet the site’s unique needs and building load requirements. Specifications are data-backed, ensuring materials can withstand chemical attack and provide a long-term protective envelope.
PE-Stamped Drawings and Construction Documents
The culmination of the design phase is a comprehensive set of PE-stamped drawings and construction documents. These include detailed layouts showing membrane overlaps, sealing details, vent pipe routing, foundation penetrations, and monitoring port locations. These documents serve as the authoritative blueprint for construction, outlining precise installation methods and quality control checkpoints. The involvement of licensed Professional Engineers (PEs) signifies that the design meets stringent engineering standards and is fit for purpose, providing an essential layer of assurance for developers and general contractors. This level of detail is critical for seamless integration with the overall building construction schedule and for navigating construction inspection requirements.
Phase 3: Expert Installation and Quality Assurance
The execution of the design requires specialized expertise and rigorous adherence to specifications. This phase is where the engineered solution is brought to life, with meticulous attention to detail ensuring the system’s long-term performance.
Specialized Installation Techniques
Installation teams, experienced in environmental construction standards, precisely follow the PE-stamped plans. This involves careful preparation of the sub-slab surface, expert placement and sealing of vapor barrier membranes, and the proper installation of vent pipes and collection layers. Seams are thermally welded or chemically bonded to create an impermeable barrier, with particular attention paid to sealing around foundation penetrations, column footings, and utility entries—common points of failure if not addressed correctly. For active systems, electrical connections and fan installations are executed to code, ensuring operational efficiency and safety. This battle-tested expertise from years of solving complex challenges means anticipating potential issues before they arise.
Post-Installation Verification and System Startup
Upon completion of the physical installation, a critical phase of post-installation verification commences. This typically includes visual inspections, smoke testing of the vapor barrier to confirm seal integrity, and pressure field extension (PFE) testing for sub-slab depressurization systems. For active systems, fan operation is verified, and initial pressure readings are taken. This data-driven verification ensures the system is functioning as designed and provides a baseline for future monitoring. Regulatory agencies often require this verification data as part of the project closeout.
Long-Term Performance and Monitoring
A successful vapor mitigation project doesn’t end at installation. Ongoing monitoring and maintenance are crucial for ensuring the long-term efficacy of the system. This often involves real-time monitoring solutions that provide continuous data on system performance, allowing for proactive adjustments and maintenance. For multi-family properties, this diligent oversight safeguards occupants and preserves property value over decades.
By following this comprehensive vapor mitigation project walkthrough, developers and general contractors can confidently navigate the complexities of environmental remediation, ensuring their projects are built on a foundation of safety, compliance, and engineering excellence. The integration of PE-stamped designs, regulatory expertise, and battle-tested installation practices is not a premium, but a standard for successful brownfield development.